Activity 2.3 - Biosphere and Interconnections
- Brendan Allen
- Sep 21, 2021
- 5 min read
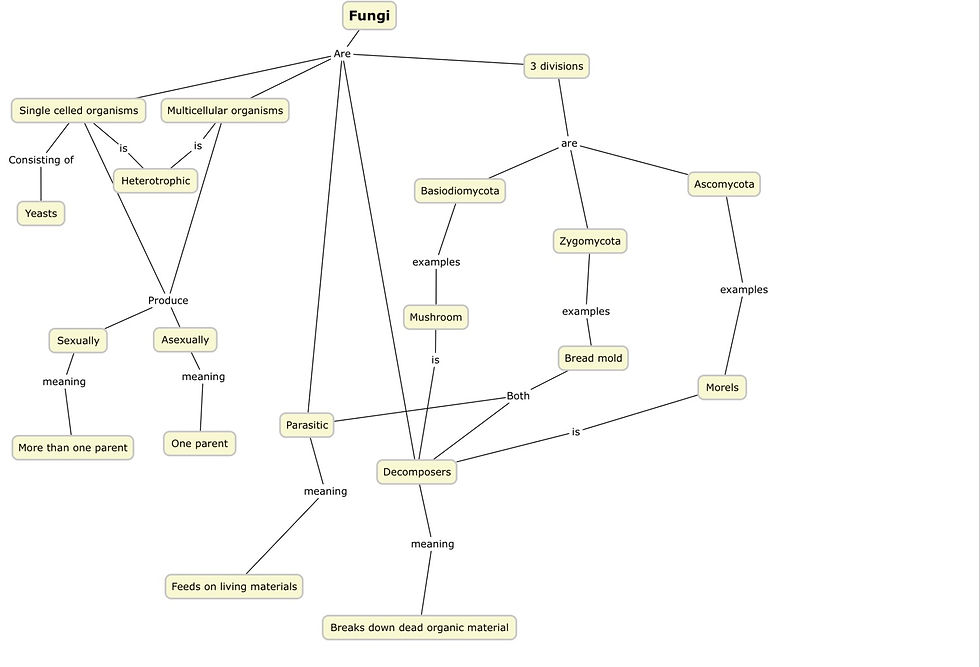
The 5 kingdoms of living organisms are classified based on their characteristics such as its cell structure, mode of nutrition, way of reproduction, and its body organization. The 5 kingdoms are Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia and each of their respective kingdoms all share the same characteristics or are very similar. Fungi for example can be both single celled like yeast and multicellular organisms such as normal edible mushrooms, but all fungi are heterotrophs meaning it gathers nutrients from simple organic substances. Two ways that fungi break down organic substances can be either decomposition which is when the organic material is broken down from a deceased organism. Another way would be parasitic in which the fungus feeds and breaks down a plant or animal while it’s living. This makes fungi ecologically important because they make excellent decomposers by recycling nutrients and reducing the amount of dead biomass.
Fungus are also split into 3 different groups based on the way the fungi reproduce. The three groups of fungi are Ascomycota which contain about 30,000 species in this division, Zygomycota which has about 600 species, and the Basiodiomycota including about 16,000 named species. Examples of a Zygomycota would be bread mold which can feed on both living and dead because its multicellular and because of the yeast is also considered single cellular can be both a decomposer and also a parasite. Ascomycota is a morel which has a honeycomb like appearance and are edible, and since most parasitic fungus cause illness and may eventually kill the host. Fungi can also reproduce sexually in which the fungi goes through three stages being: plasmogamy, karygamy, and meiosis. Not only that but they can also reproduce asexually as well by forms of either fragmentation, fission, budding, and spores which is what majority of fungi that reproduce asuxually do.

Ecosystems are a community of organisms that interact with their environment. Ecosystems however, are a part of a more broad spectrum. When narrowing down an ecosystem biomes are then established, and biomes are regions of land that are given certain conditions in order to classify them. Biomes are then characterized by the life forms of the most dominant organisms. Most land biomes are identified by the maturity or growth of the vegetation while aquatic biomes are generally classified based on their dominant animals. The 3 classifications of biomes are terrestrial, freshwater, and marine biomes.
The freshwater biomes consist of the wetlands, and the wetlands are classified as shallow, flooded places on land with most plants rooted within the sediment and are able to grow several meters. Types of wetlands are influenced by the amount of permanence of surface water and the amount of nutrients Because of the water level being higher than the floor the water is usually brown and hard to see the floor below. Within the wetlands there are 4 major types of environments included. One of the four environments within the wetlands are marshes. Among the 4 environments in the wetlands marshes are the most productive containing plants such reed, cattails, and bulrushes. Marshes also have open water areas where there are floating plants such as water lilies and lotuses. Swamps which are more forested are dominated by silver maple trees, white elm, or bald crypress, and marshes are either seasonally or permanently flooded. Both fen’s and Bogs are developed within cool, wet climates however, Fen’s compared to bogs are seen to be less acidic meaning that fen’s typically have more nutrient supply. Bogs are also less productive compared to fen’s due to the fact that the acidity is higher because bogs are only fertilized through the atmospheric inputs of the dust and chemicals that dissolve in the water.

Within an ecosystem plants and animals interact with each other and create an ecological food chain that shows the direct feeding relationship of the animal and plants. However a food web can show connection amongst all the food chains within the ecosystem for instance a person might eat an apple or fruit on top of their usual diet of beef or fish making that person both a secondary consumer and a tertiary consumer.
At the start of the food web is the sun. When the solar energy of the sun is absorbed by the zooplankton, phytoplankton, and plants at the top of the water energy, those organisms convert that energy into food for themselves making these organisms the first or primary consumers. Ducks and fish on top at the surface of the water feed on the plants while the phytoplankton and zooplankton are preyed upon by the small crustaceans and other bottom feeders like clams. This makes the crustaceans, duck, and the fish secondary consumers and then humans or bald eagles can eat these organisms making them the tertiary consumer so on and so forth. However the duck may also feed on the fish making the ducks both a secondary and tertiary. As you progress further up into the food chain or web the amount of organisms in each category tends to get lower while there is an abundance of primary producers and consumers. The reason for this is because of the law of thermodynamics, whenever an organism is consumed the amount of energy that is lost during the transfer is about 90%. This 90% loss applies to every time energy is transferred to the next organism making it so more productivity needs to occur which requires energy. In every ecosystem productivity by autotrophs is always greater than that of the herbivore and predators
Connection
All over the world there are various ecosystems and regions that are categorized based on the dominant plant or animal of that biome. Biomes are the very basics of the environment as it only describes the type of area and type of living organisms in that area. The freshwater biome consists of wetlands, and within the wetlands there are 4 individual regions of which the most productive and nutrient one being the marshes. In the marshes there are plants and organisms such as cattails, algae, shrimp, bass, heron, and muskrats.
In the marshes as the sun gives off its solar energy the algae and cattails below absorb that energy and use that energy to create food and nutrients for themselves. The fish at the top of the water feeds on the cattails while the shrimp at the bottom feed on the algae making the fish and shrimp secondary consumers. After this the heron or a muskrat might fish out one of the secondary consumers making them a tertiary consumer. Fish may also feed on the shrimp not only making the fish a primary but a secondary consumer as well turning a food chain into a food web.
At the end of every food chain though the remains of the animals then sink to the bottom of the marsh and below there are fungi there also known as decomposers. Within the wetland of the freshwater biome the climate is usually a hot humid environment which is a rich environment for fungi to grow in. Fungi are either a single or multicellular organism but both are heterotrophs meaning they feed on simple organic substances and are either decomposed or a parasite. A fungi that decomposes breaks down material that is already dead and will only break down the remaining nutrients recycling it back into the earth. A parasitic mushroom will feed on a living organism continuously breaking it down until it dies.

Comments